High blood sugar can damage your body parts, known as complications of diabetes. You can prevent or delay many of these complications.
Diabetes is a chronic medical condition marked by elevated blood sugar levels due to either insufficient insulin production or ineffective use of insulin by the body. The primary symptoms include increased thirst, frequent urination, fatigue, and blurred vision. Diabetes is the result of obesity, sedentary lifestyle, autoimmune reactions and genetic conditions. There are three main types of diabetes: type 1, type 2, and gestational diabetes.
Type 1 diabetes occurs when the immune system attacks and destroys insulin-producing cells in the pancreas. Type 2 diabetes results from insulin resistance, where the body’s cells do not respond properly to insulin. Gestational diabetes develops during pregnancy.
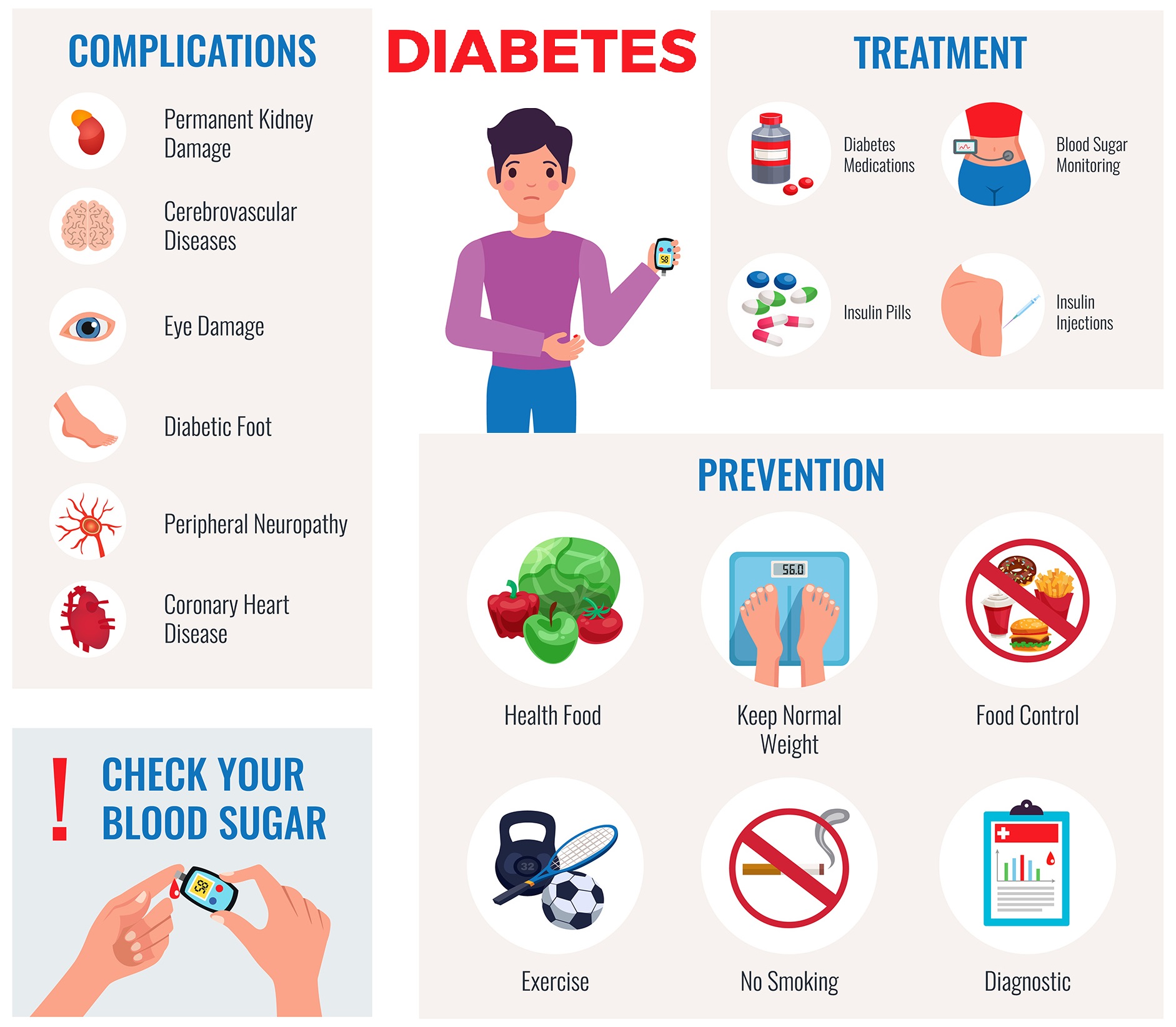
While diabetes is not curable, it is manageable through lifestyle modifications, medications, and insulin therapy. If diabetes is not controlled, it can lead to various serious complications affecting different parts of the body.
What Are the Major Complications of Diabetes?
Diabetes can result in a range of complications, which can be categorized into chronic and acute forms. Chronic complications develop gradually over time and can cause significant damage if left untreated.
These complications include heart disease, neuropathy, nephropathy, retinopathy, foot complications, skin conditions, and dental issues. On the other hand, acute complications can occur suddenly and pose immediate risks.
These include hypoglycemia and hyperglycemia, which can lead to severe consequences such as diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) and hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state (HHS).
Here are the common complications of diabetes:
Eye Problems (Retinopathy)
Diabetic retinopathy, a common complication of diabetes, can lead to vision impairment if left untreated. Regular eye screenings are crucial for early detection and timely intervention. With prompt treatment, the progression of retinopathy can be halted, preventing permanent vision loss.
Foot Problems
Foot problems are common complications of diabetes, often arising from nerve damage (neuropathy) and poor blood circulation. These issues increase the risk of foot ulcers, infections, and, in severe cases, amputation. Proper foot care, including daily inspection, regular visits to a podiatrist, and wearing comfortable shoes, is crucial for preventing complications and maintaining foot health in individuals with diabetes.
Heart Attack and Stroke
Individuals with diabetes are at an increased risk of heart attack and stroke due to factors such as high blood pressure, high cholesterol levels, and narrowed blood vessels. Diabetes accelerates the development of atherosclerosis, a condition where plaque builds up in the arteries, leading to blockages. This increases the likelihood of heart attacks and strokes.
Kidney Problems (Nephropathy)
Kidney problems, known as nephropathy, are common complications of diabetes. Persistently high blood sugar levels can damage the tiny blood vessels in the kidneys, impairing their function over time. If left untreated, this damage can lead to chronic kidney disease and eventually kidney failure. Symptoms may include swelling in the ankles, decreased urine output, and fatigue.
Nerve Damage (Neuropathy)
Nerve damage, also known as neuropathy, is a common complication of diabetes. High blood sugar levels can injure the nerves throughout the body, causing symptoms such as tingling, numbness, or pain, typically starting in the feet and gradually spreading upwards. This condition can lead to serious complications like foot ulcers, infections, and even amputations if left untreated.
Gum Disease and Other Mouth Problems
Gum disease and other mouth problems are common complications of diabetes. High blood sugar levels can contribute to bacterial growth, leading to inflammation, infection, and gum disease. Proper dental hygiene, regular dental check-ups, and controlling blood sugar levels are essential in preventing and managing these oral complications in individuals with diabetes.
Sexual Problems in Women
Diabetes can lead to sexual problems in women, including decreased libido, vaginal dryness, and difficulty achieving orgasm. These issues often arise due to nerve damage, reduced blood flow to the female genitals, and hormonal imbalances associated with diabetes. Prevent Vaginal infections with these reproductive tips!
Sexual Problems in Men
Diabetes can contribute to sexual problems in men, such as erectile dysfunction (impotence), reduced libido, and ejaculatory issues. These complications arise due to nerve damage, impaired blood flow to the male genitals, and hormonal imbalances associated with diabetes.
Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA)
It occurs due to high levels of ketones in the blood, leading to acidosis. It typically occurs in individuals with type 1 diabetes when insulin levels are too low, causing the body to break down fat for energy instead of glucose. DKA requires immediate medical attention to prevent life-threatening complications such as coma or death.
How Do I Prevent or Delay Diabetes Complications?
Proper management can prevent or delay diabetes complications. To reduce the risk, keep your blood sugar, blood pressure, and blood fats in control.
If you smoke, quitting can significantly reduce the risk of complications such as heart disease and stroke. Adhere to the prescribed medications and indulge in low-glycemic foods to keep your glucose levels normal.
Understanding the care you need when living with diabetes and adhering to it diligently can help prevent or delay the onset of complications.
What Are the Best Medications for Diabetes Management?
The selection of medications for diabetes management, whether Type 1 or Type 2, depends on various factors such as health status, medical history, lifestyle, and disease severity.
For Type 1 diabetes, insulin therapy is fundamental, administered through injections or insulin pumps to regulate blood sugar levels.
Type 2 diabetes treatment often starts with lifestyle adjustments but may progress to medications like metformin, enhancing insulin sensitivity and reducing liver sugar production.
Additionally, drugs like glipizide and glimepiride stimulate insulin release from the pancreas. Vildagliptin increases incretin hormone levels, regulating blood sugar, while pioglitazone hydrochloride improves insulin sensitivity in muscle and fat tissues. These medications play vital roles in managing diabetes, aiding glucose control and minimizing the risk of complications.
These diabetes medicines can be procured by ordering online through medicine delivery apps. The online purchase makes healthcare seamless and delivers medicines to your doorstep on time. If you order from an online pharmacy app like Truemeds, which offers generic substitutes, you can save a lot on your diabetes medicines expenses.
Takeaway
The major complications of diabetes include heart disease, kidney disease, nerve damage, and eye disease. Acute complications like diabetic ketoacidosis can also occur, which can be fatal.
If you have diabetes, you should maintain healthy blood sugar levels through diet, exercise, and adherence to medicines. Regular monitoring of blood sugar, blood pressure and cholesterol levels can help you proactively manage your condition.
Additionally, avoiding tobacco use, managing stress, and maintaining a healthy weight can help reduce the risk of diabetes-related complications.



