Some emergent symptoms in pregnancy include heat exhaustion and heat stroke due to many reasons like increase in blood volume; alterations in pregnancy-related hormones; and limitation of heat dissipation by the body. Pregnancy per se is another condition that alters a woman’s body in one way or the other making her more vulnerable to these illnesses.

Using the information presented here, we looked at the contributory factors to heat related disorders in pregnant mothers and the common symptoms associated with heat exhaustion and stroke in pregnancy.
You will also explore measures put in place to prevent such complications, the significance of proper diet and nutrition during pregnancy. Also learn about how pregnant mothers can recognize the need for medical assistance in cases of heat exhaustion and stroke across the various trimester.
What is Heat Exhaustion?
Heat exhaustion is a condition whereby the body is unable to control its temperature and some of the symptoms include but are not limited to sweating, high blood pressure, weakness, dizziness and cold skin. The reason behind this condition is that often this condition can arise because of overheating exposure, lack of proper hydration and involvement in heat related activities in hot climates.
What is Heat Stroke?
Heat stroke, which is a more serious heat- related disease, is considered the most severe form of heat injury. It happens when the thermostat of the body goes out of order or has a break down and brings the core body temperature to 104 degrees Fahrenheit or 40 degrees Celsius and above. Which if left untreated can cause confusion, loss of consciousness, seizures and in severe cases – death. Heat stroke, like any other heat illnesses, calls for professional help.
Also Read: Most Common Pregnancy Complications: Signs and Symptoms
Why Pregnancy Increases Susceptibility
- Increased Blood Volume: Pregnant women have been observed to have their blood volume swell up to 50 percent in order of support the developing embryo and for labor. Elevated blood flow hands the body the ability to sense this feel of heat than normal.
- Hormonal Shifts: Because estrogen and progesterone are produced during pregnancy, they can affect the thermoregulation and thereby subjects the body pregnant women to heat stress.
- Higher Basal Metabolic Rate: During pregnancy, metabolism increases the basal metabolism, and the body’s energy requirements increase at rest. It can lead to the generation of heat inside the body.
- Limited Heat Dissipation: They explained that as the size of the uterus increase it puts pressure on the blood vessels, causing them to tighten and close down to allow little blood circulation in the skin – then the body cannot sweat and release heat.
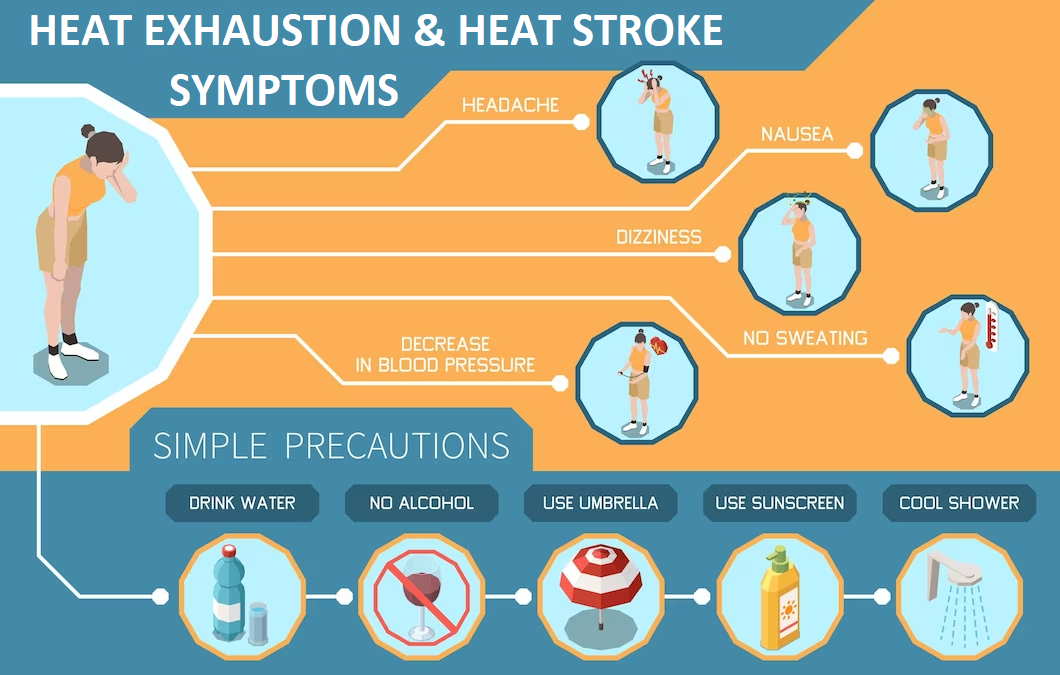
Symptoms of Heat Exhaustion
- Excessive sweating
- Pale, clammy skin
- Muscle cramps
- Fatigue or weakness
- Headache
- Dizziness or lightheadedness
- Nausea or vomiting
- Fainting spells
Symptoms of Heat Stroke
- Hot, dry skin (lack of sweating)
- Red or flushed appearance
- Rapid heartbeat
- Confusion or disorientation
- Slurred speech
- Seizures
- Unconsciousness
Risks Associated with Heat Exhaustion and Stroke in Pregnancy
For pregnant women, heat exhaustion and stroke can pose a range of risks, including:
- Preterm Labor: Heat exhaustion and stroke can cause a woman’s body temperature to increase and this may cause contractions of the uterus or premature labor. This can result in early onset of labor and a baby that is not fully mature to be delivered may have under developed organs and lungs that may require hospitalization in NICU.
- Low Birth Weight: If a woman suffers heat exhaustion or a heat stroke, the chances are increased that her baby will arrive prematurely and with a decreased birth weight with the baby in turn being prone to further health problems in the perinatal period.
- Neural Tube Defects: Elevated prenatal maternal temperature has been signified more often neural tube defects like spina bifida and anencephaly in new born babies. Such conditions lead to life time disabilities such as paralysis, incontinence and mental retardation.
- Maternal Complications: Heat exhaustion and heat stroke can also affect the mother whose body gets dehydrated, develops abnormal levels of electrolytes and even results to kidney failure and possible death.
Prevention Strategies: Staying Cool During Pregnancy
- Hydration is Key: Take plenty of water and any other right fluid for you to be able to have a well hydrated body. It is recommended that man should be intaking no less than 8-10 glasses of fluids per day based on physical activity and its rate of sweating.
- Dress for Comfort: Dress lightly and in light-colored garments and wear natural fiber clothing, especially cotton. You know that lighter colors are reflective of sunlight than color of darker hues.
- Avoid Peak Heat Hours: Avoid going out during midday sun that is from 11 in the morning to 5 in the evening as it is when sun’s intensity is highest.
- Cool Down Quickly: Relax often in an air cipher area to lower your body temperature as fast as possible.
- Limit Physical Exertion: If it is blazing sun, try and avoid very heavy exercise or other heavy physically demanding work. Just exercising those muscles that don’t put too much pressure on the limbs or doing your activities at home.
- Monitor Indoor Temperatures: Make sure the indoor temperature is good, to be able to utilize the fans, air conditioning or whatever heat source.
- Recognize Personal Limits: Learn the signals that your body sends to you to know when you need to make a break. If you have suffered heat stroke, syncope or heat cramps in the past then you should be more cautious.
Nutritional Support to Combat Heat Stroke
- Hydrating Foods: If you find yourself sweating a lot during exercise, you’ll want to replace the fluids and electrolytes lost by eating more foods high in water like watermelon, cucumber, and vegetables.
- Electrolyte-Rich Foods: Include sports-replenishable foods that are rich in electrolytes like potassium, magnesium and sodium but depleted from our system through excessive sweating like bananas, spinach and almonds.
Avoid Dehydrating Foods: Reduce your consumption of diuretic foods and drinks that include caffeine and alcohol as they only worsen your condition.
When to Seek Medical Attention
If you have fever, confusion, or a seizure, and you notice signs of heat stroke then go to the hospital immediately. Heat stroke is a dangerous condition, and very often it may lead to a fatality, and it should be treated as soon as possible.
Emergency signs:
- Persistent high fever
- Difficulty breathing
- Fainting
- Severe confusion
If one has continued heat exhaustion, then it is advised not to rest for half an hour then get medical attention and if there are signs of heat stroke then the best thing is calling an ambulance. In a hospital, therapy may involve; administration of intravenous fluids, use of blankets or other major tools aimed at regulating body heat.
Managing Heat in Different Trimesters
- First Trimester: Stick with the goal of creating healthy hydration patterns and paying attention to signs of heat stress tolerance. Begin adding or reducing some of the more involved cooling measures or resting back further down on the scale of physical and mental activity.
- Second Trimester: Go on with those steps of precautions and add one more; try fanning the liquid or putting it in the refrigerator. Be careful, however, of the heat due to increased levels of exertion.
- Third Trimester: During your second trimester, be sure to avoid sweating too much, use air conditioning, eat a lot of water-rich foods, and rehearse much less in hot climates. Avoid heat exposure during the last few weeks of pregnancy since the body’s ability to dissipate heat is reduced further.
Myths and Misconceptions
There are several myths relating to heat management during this time of pregnancy. Let’s debunk a few:
Myth: Pregnant people shouldn’t drink too much water.
Fact: Keeping well-hydrated is important and can minimize problems.
Myth: Sweating means you’re staying cool.
Fact: Loss of fluids, heat exhaustion and even cold sweat could happen if you sweat ‘to the extent of dropping a lot of ‘sweat.’
Myth: Sunscreen protects against heat stroke.
Fact: Even though sunscreen application helps to avoid sunburn, it does do nothing to maintain human body temperature.
The Role of Partners and Caregivers
Excited mothers are closely surrounded by their partners and caregivers always to ensure that they too do not pose any danger to their own selves. Here are some ways in which they can assist:
- Monitor body temperature: Monitory the mother’s temperature regularly, especially during warm weather or after some exercise. Tell her to take a break in an air-conditioned area and that for the rest of the day she be drinking plenty of water.
- Provide a comfortable environment: It will be important to make sure the mother’s environment is well aired and having a fan or air conditioner will help keep the environment cool.
- Encourage rest: Pregnancy is a special kind of health need and the partners and caretakers of the expectant mothers should ensure that the woman take as much rest as she requires.
- Promote a healthy diet: A pregnant woman should avoid foods high in fat, sugar, and salt while taking foods such as fruits, vegetables, lean meats, and whole grain products to help moderate heat exposure during pregnancy.
- Educate themselves: A caregiver and a partner should make sure that they were informed on how to identify the different signs indicating heat exhaustion and heat stroke, adequate fluid intake and heat regulation.
Conclusion
Pregnant women should avoid heat exhaustion and heat stroke due to dangers associated with these conditions. It would help if to enhance the awareness of the causal factors of heat illness, the signs, and the preventive measures that pregnant woman can take to reduce their vulnerability while pregnant.
Once again look at the guidance – proper drinking, correct outfit, heat regulation, and monitoring are critical to preventing heat exhaustion and heatstroke during pregnancy.
However, this is only possible when a woman undergoes a medical checkup should she be experiencing severe symptoms to get early treatment as this is very dangerous for both the mother and the unborn child.


