Failure to install NVIDIA drivers creates frustration for users who need to improve system performance through optimized graphics capabilities. Every user faces difficulties with failed driver installations that cause significant obstacles to system performance regardless of their daily activities or professional role. The good news? Several procedures exist that help users fix this specific problem. Finding the root cause always leads to a successful solution.
The guide presents a systematic approach to solving NVIDIA driver installation problems. Careful execution of these methods will allow you to operate your drivers without facing any inevitable stress. Complete resolution of both simple and complex compatibility problems is possible under our assistance. Let’s begin the process of enhancing your system’s graphical performance until it reaches its full potential.
Common Causes of NVIDIA Driver Installation Issues
Before diving into solutions, let’s understand some of the reasons why NVIDIA drivers might not install:
- Corrupt or Incompatible Drivers: Downloading the wrong version of the driver or corrupted files can prevent installation.
- Windows Updates Interference: Pending Windows updates may block or interfere with driver installation.
- Existing Driver Conflicts: Previous NVIDIA drivers might cause conflicts, leading to installation failures.
- Antivirus or Firewall Interference: Security software might block driver installations.
- Faulty or Corrupt Windows System Files: System corruption can prevent the driver from installing properly.
- Incorrect BIOS Settings: Some BIOS configurations might impact the GPU driver installation.
Pre-Installation Checklist
Perform this step-by-step guide as your first measure before attempting any fixes.
- Verify System Compatibility: Make sure your GPU and Operating System match the driver version that you aim to install.
- Update Windows: A full system update needs to be completed before adding the driver installation.
- Uninstall Previous Drivers: You should remove all existing and corrupt NVIDIA drivers through an uninstall process.
- Disable Antivirus and Firewall: Antivirus software should be disabled before installation as they may interrupt the process.
- Download the Driver from NVIDIA’s Official Website: Users should download the driver exclusively from NVIDIA’s Official Website because this ensures the files are not corrupted.
Step-by-Step Fixes for NVIDIA Driver Installation Issues
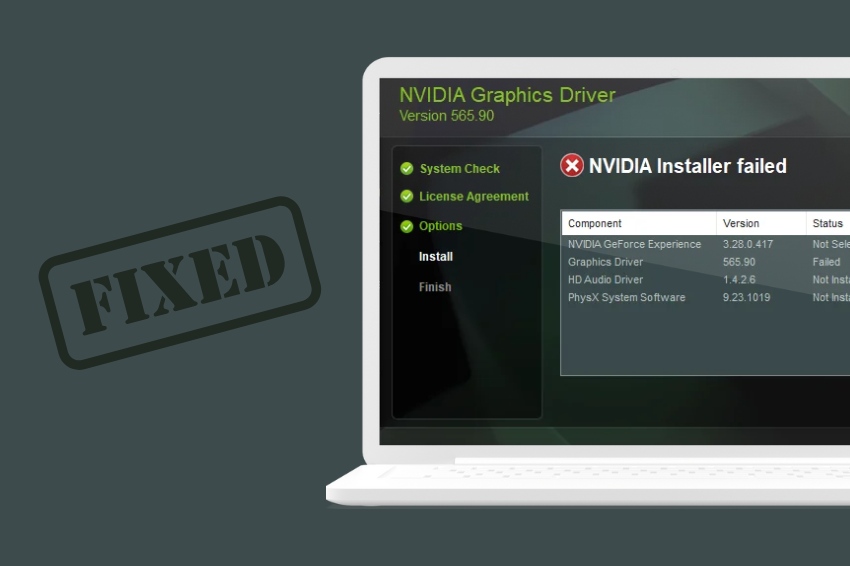
The problem of NVIDIA drivers failing to install affects numerous users. Users frequently meet installation errors which lead to their system frustration and prevent them from utilizing their GPU to the fullest. This solution guide presents multiple fixes to successfully install NVIDIA drivers and bypass installation failures and infinite loops while resolving error messages.
Solution 1: Uninstall Previous NVIDIA Drivers Completely
A complete NVIDIA driver removal needs to occur before starting an installation.
Steps to Uninstall NVIDIA Drivers
- Press Windows + R, type appwiz.cpl, and hit Enter.
- In the Programs and Features window, locate NVIDIA Graphics Driver.
- Right-click and select Uninstall.
- Restart your computer.
For a more thorough removal:
- Download Display Driver Uninstaller (DDU) from the official site.
- Boot into Safe Mode (Press Shift while clicking Restart > Troubleshoot > Advanced options > Startup Settings > Restart > Press F4).
- Run DDU and select Clean and Restart.
Solution 2: Download and Install the Correct NVIDIA Driver
The usage of incorrect driver version during download may lead to installation issues. Follow these steps to get the correct version:
- Go to NVIDIA’s official website.
- Enter your GPU model, OS, and preferred driver type (Game Ready or Studio Driver).
- Click Search, then download the latest recommended version.
- Run the installer as Administrator.
Solution 3: Disable Windows Automatic Driver Installation
The operating system of Windows has a habit of placing generic GPU drivers that create problems during NVIDIA driver installation.
Steps to Disable Automatic Driver Installation:
- Open Control Panel > System and Security > System.
- Click Advanced system settings on the left panel.
- Go to the Hardware tab, then click Device Installation Settings.
- Select No (your device might not work as expected) and click Save Changes.
Solution 4: Install NVIDIA Drivers Manually via Device Manager
If the standard installation method fails, try installing manually:
- Press Windows + X and select Device Manager.
- Expand Display adapters, right-click your NVIDIA GPU, and choose Update driver.
- Select Browse my computer for drivers > Let me pick from a list.
- Click Have Disk and locate the driver folder (usually found in C:\NVIDIA after running the installer).
- Select the .inf file, then click OK.
Solution 5: Disable Antivirus and Windows Defender Temporarily
Some security software can interfere with driver installation.
- Disable Windows Defender:
- Press Windows + I to open Settings.
- Navigate to Update & Security > Windows Security > Virus & threat protection.
- Click Manage settings and turn off Real-time protection.
- Disable Third-Party Antivirus:
- Open your antivirus program and look for a disable
- You may need to temporarily uninstall it if disabling doesn’t help.
Solution 6: Run Windows Updates
Updating Windows can resolve compatibility issues with NVIDIA drivers.
- Press Windows + I to open Settings.
- Go to Update & Security > Windows Update.
- Click Check for updates and install any pending updates.
Solution 7: Install Drivers in Safe Mode
Booting into Safe Mode can eliminate potential software conflicts.
Steps to Enter Safe Mode:
- Press Windows + R, type msconfig, and hit Enter.
- In the Boot tab, check Safe boot and select Minimal.
- Click Apply and restart your computer.
- Once in Safe Mode, try running the NVIDIA driver installer.
Solution 8: Check for Windows Corruption with SFC and DISM
If system files are corrupted, they can block driver installations.
Run SFC (System File Checker):
- Open Command Prompt as Administrator.
- Type sfc /scannow and hit Enter.
- Wait for the scan to complete and restart your computer.
Run DISM (Deployment Image Servicing and Management):
- Open Command Prompt as Administrator.
- Run these commands one by one:
- DISM /Online /Cleanup-Image /CheckHealth
- DISM /Online /Cleanup-Image /ScanHealth
- DISM /Online /Cleanup-Image /RestoreHealth
- Restart your PC and try reinstalling the NVIDIA driver.
Solution 9: Check Your BIOS and Enable Discrete GPU
Your BIOS configuration could block the correct functioning of NVIDIA driver software.
- Restart your PC and enter BIOS/UEFI (Press F2, F12, Del, or Esc during startup).
- Look for Graphics Configuration or GPU Settings.
- Ensure Discrete GPU is enabled.
- Save changes and restart your PC.
Solution 10: Perform a Clean Boot
A clean boot state removes all background applications because it prevents them from interrupting the installation process.
Steps to Perform a Clean Boot:
- Press Windows + R, type msconfig, and hit Enter.
- Go to the Services tab, check Hide all Microsoft services and click Disable all.
- Switch to the Startup tab and open Task Manager.
- Disable all startup programs.
- Restart your PC and try installing the NVIDIA driver.
Final Thoughts
Users should apply several troubleshooting methods when fixing NVIDIA driver installation problems, including validating system compatibility and performing manual driver installation. Persistence is the main principle for using DDU and Windows Update checks to resolve software issues and deal with conflicts in driver installation.
A system restart combined with administrator privileges or disabled antivirus settings can serve as a solution that fixes driver installation problems when other measures do not work. The main thing? The solution requires a step-by-step method where you rule out different causes until a working solution reveals itself.
Technology shows the actual fault and software installations do the same. If installation issues persist, you should consult professionals on the NVIDIA forum or seek assistance. Each installation attempt gives you unique troubleshooting capabilities that will benefit other technical challenges beyond this single operation.
Although these problems are troubling, they also provide an opportunity to understand the complex nature of contemporary computing systems because fixing drivers involves understanding broader system operating principles.