In the world of physical education, seeding is a term that dictates the fundamental approach toward the further development of environment and growth of those who are interested in physical activity, regardless of their talents. Educators and coaches seek to use seeding strategies to make the total teaching-learning process of physical activities achieve the goals of accommodating all clients or students through the positive challenge factor.
This article focuses on what seeding is, its role, different approaches, advantages, limitations, and possibilities of using it in physical education.
What is Seeding?
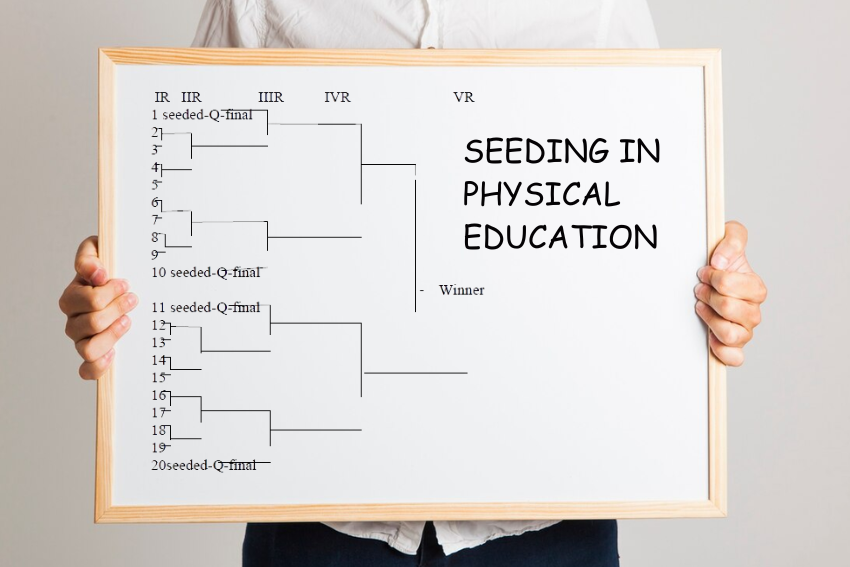
Seeding in physical education encompasses the process of forming balanced teams/closed categories with the help of participants’ various criteria. “Seeding is meant to provide balance, bring equal chances of success and create conditions conducive for development of all participants.” This is a procedure that looks into skill capability, age, experience and strength to create teams or groups that enable participants to be challenged yet not overworked.
Seedling is not only used in competitive games; it can also be used in games that do not involve competition to encourage large participants. The assessment of learning to strengths and weaknesses of each participant enables creation of mood that is conducive of personal development as well as establishment of team work.
Importance of Seeding in Physical Education
Let’s understand the importance of seeding in physical education by adjusting methods for determining the performance of students, leading to proper competition and development of the effective technique to involve students in sports.
- Equal Opportunities: This element enhances an equal opportunity that gives the chances of participation among all the participants about determining equal exercises. This way, it is possible to control the effect of enthusiastic and active learners who always want to control the flow of the classes and ensure that they make their teammates work together in groups.
- Skill Development: Competent seeding also ensures that the participants get to face a good level of challenge. This kind of learning promotes skill enhancement and honing since people are not too much challenged or too bored.
- Increasing Confidence and Motivation: This is because, when the participants are grouped according to their performance standards, confidence and motivation levels will improve. This method of motivation encourages people to continue participating as well as improving themselves.
- Inclusiveness and Social Interaction: Seeding also increases participants’ interaction by making sure that everyone is involved in the game. This inclusive approach fosters social interaction and teamwork, essential components of physical education.
- Reducing Frustration and Disengagement: This refers to a situation where participants feel frustrated and begin to withdraw or disengage themselves due to being placed in an incorrect class. Seeding contributes to the abolishment of these factors because people have a feeling of self-worth, and capability.
Methodologies of Seeding
Seeding methodologies are different for the activities depending on the goals and the participants involved. Here are some common approaches:
- Skill-Based Seeding: In this method of selection the participants are segregated according to their abilities at a certain level in the sport or activity. An example of such methods includes skill assessments, previous performance records, or teacher observations on the performance of candidates.
- Age-Based Seeding: Age is the simplest criterion to use when grouping participants especially the children. This is because this approach considers the physical and cognitive developmental phases of the participants.
- Mixed-Seeding: This is a system of seeding whereby teams are drawn in such a way that the various factors like skills and age are also taken into consideration. This approach can raise the rate of many-faceted interactions within teams and make them more intensified.
- Random Seeding: Random seeding is used in some cases to increase the level of expectation and fun included in the game. It is not suitable for providing competitive balance but may be good for equality and eliminating prejudices.
- Rotational Seeding: in this approach, teams or groups have to be rearranged on a rotational basis in an effort to ensure that participants work with different co-participants and encounter different problems. This rotation is useful to avoid stagnation and promote the organization to be more adaptable in its work.
Benefits of Seeding
Learn how seeding in physical education can benefit learners from being able to play the game fairly as well as improving on the skills possessed and the team work among them besides changing the learners’ mind set towards growth.
- Greater Interaction: The formation of equitable and moderately difficult groups by seeking to retain interest in the activity among the participants.
- Better interactions: Due to seeding, every member can contribute towards the operations of the team and hence improved interactions. This integration improves the learning process and results in the best experience that any group of students can get.
- Generalized Anomaly: It also means that through seeding, strategies can be developed to follow a structured plan that best suits the students in each group to ensure maximum growth of the learner.
- Improved Psychological Results: Participants who remain in well-seeded grounds that make them successful and gain recognition are likely to develop a positive attitude towards body activities and this has long-term effects on their health.
Challenges of Seeding
Learn more on challenges of seeding strategies that the opportunity in allocating resources, the environment, and advanced technologies on matters concerning yield.
- Assessment Accuracy: It can also be equally difficult to find high levels of accuracy when attempting to assess the participants’ skills and skills. This means that the assessment results can cause imbalance within the teams and negatively affect the concept of seeding or ranking.
- Flexibilities: Skills of the participants maybe dynamic and therefore the seeding arrangements may need to be reviewed from time to time. If it is true that teaching is an evolving process that is contrary to all ethereal ideals one must be prepared to be much more flexible than before to give a constant lookout to constantly varying conditions.
- Perceived Unethical Nature: Some of the participants Iftikhar et al. (2012) stated that they feels that seeding is unfair and especially a person feels that they are put in the lower base skill group. It is therefore important to be clear to rectify these issues through an enhanced understanding and being truthful, especially to clients.
- Resource Limitations: Some of the important steps involved in seeding may occupy more time than expected and may therefore call for other complementary resources such as time for the carrying out of assessments and other planning processes. They can in turn hardly meet the above demands due to their other roles and obligations as teachers.
Practical Applications for Seeding
Uncover ideas on how to turn strategic seeding as one of the primary means of improving growth, visibility, and success of your projects in various industries.
- In School Physical Education Programs: Seeding is also widely used in school physical activities and games in order to make sure that all the children can realize the maximum potential of their physical education’s classes. For this reason, it is obvious that positive factors, resulting from the balanced teams formed by educators provide an effective learning environment.
- In Youth Sports Leagues: It is used in youth sports leagues were several teams need to be grouped into divisions to ensure that tough teams are grouped together but at the same time they have a reasonable opponent to face during the league’s competition. It is effective in the process of enhancing the skills of young athletes and still have fun and make friends.
- In Community Recreation Programs: Seeding is used in most community recreation programs to suit the ability of all the participants in different activities offered for recreation.
- In Corporate Wellness Programs: It also applies in corporate wellness programs to allocate teams that will encourage balanced working teams during events like team building and other exercises like sports days. This increases on diversity and ensures a large group of people participate.
Conclusion
Incorporation of seeds in physical education is an effective process that teachers and trainers can apply to let all students have a fair opportunity to access the activity. It would then be possible to match an individual who is wrongly placed with an activity that can motivate and stimulate their learning process and assist other team members to develop as well.
Although there is bound to be some difficulty in seeding, the benefits of this are assuming more significance than the difficulties in physical education. Thus, the process of seeding will remain pertinent strategies for developing quality teaching practices for physical education which will result in effective provision of those opportunities to all individuals as they engage in physical activities.