Urinary incontinence has become a severe problem affecting about a third of the US citizens, according to the American Urological Association. The huge number of patients is because the condition affects people of all ages, men and women alike.
The condition is often surrounded by stigmatization and social embarrassment. This is because many people don’t understand what it is and how it can be managed. Fortunately, medications and interventions can help victims manage incontinence and pursue an active life.
That said, let’s take a look at what urinary incontinence is, and its symptoms around the various types of incontinence. We’ll also explore diagnoses, procedures, and treatment options for subsequent healthy living.
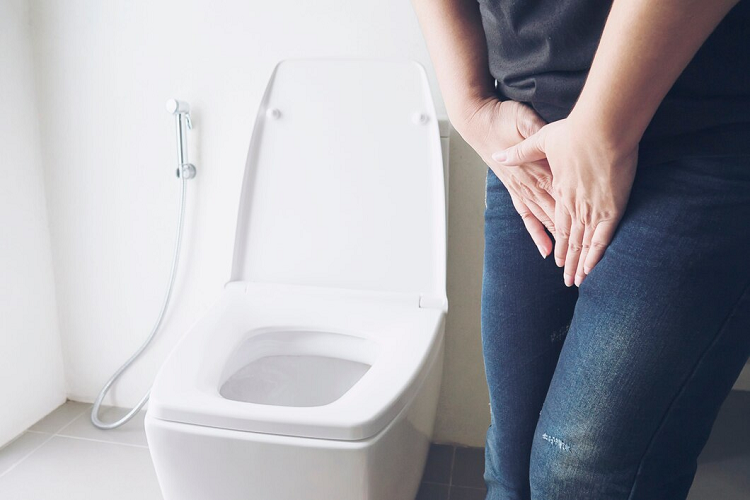

What’s Urinary Incontinence
Loss of bladder control, a problem with millions of people today, can be a sign that you are ailing from urinary incontinence. People suffering from it can’t always control how and when to urinate. Depending on the severity, you might involuntarily release small amounts of urine when you laugh or cough or experience strong urges to urinate that are often difficult to control.
Subsequently, urinary incontinence can be embarrassing, especially in social setups. It could lower your self-esteem because people become discriminative and unfriendly to you, and typically, social nonacceptance can bring more adverse effects. Moreover, it’s often difficult to perform daily activities if you have urinary incontinence issues because you’ll want to change clothes often to relax and feel a bit comfortable.
Luckily, the introduction of adult pull on diapers has made urinary incontinence care more achievable without compromising one’s daily routine or self-esteem. Typically, adult pull-ons are highly absorbent, discreet, and comfortable diapers that patients wear to manage the issue.
Moreover, pull-ons are often skin-friendly, so there are no worries that you need to take skin treatments after using them, which can add to the cost. They are also odor-free and environmentally friendly and come in various sizes.
Over the years, urinary incontinence has been a rampant issue for the aging population. Today, though, adults and children of either gender could be a victim. So, it’s crucial that everyone seeks medical care, changes lifestyles, or gets an adult diaper whenever there is a possibility they’re having the issue.
Symptoms of Urinary Incontinence
Unless we understand the various types of incontinence, we won’t understand the symptoms of urinary incontinence. So, let’s look at it. Although urinary incontinence is characterized by dysfunction of the blander, it occurs differently, and so it is grouped into six major categories.
1. Urge Incontinence
Do you often experience a sudden, uncontrollable urge to urinate? One that leads to an involuntary flow of urine in seconds? That’s probably urge incontinence, a urinating urge that comes suddenly and is impossible to ignore.
Urge incontinence occurs when the bladder muscles contract more often and at the wrong time. Ideally, the bladder assumes it is full when it’s not and releases urine. Because of its sudden nature, urge incontinence may result in frequent rounds to the bathroom to stay clean and healthy. But this can be frustrating and limiting.
Urge incontinence can result from a minor infection that affects the bladder or a more severe cause like diabetes or neurological disorder.
Fortunately, however, urge incontinence is manageable with exercises like Kegel that strengthen the bladder and urethra muscles.
2. Stress Incontinence
Stress urinary incontinence, SUI, results from triggers and activities that cause pressure on your bladder, e.g., running, lifting, exercising, sneezing, or coughing. In severe cases, stress incontinence is associated with a simple activity like sitting or walking. If you can predict your typical cause of stress incontinence, you can possibly stop the trigger that leads to the leakage. Otherwise, it can restrict your life.
Stress incontinence is common among pregnant women or lactating mothers. That’s because their urinary systems often experience pressure and, possible damage during childbirth. It is also caused by weakness of the pelvic floor muscles and urethra sphincter, which support the urethra and bladder.
3. Overflow Incontinence
Overflow is caused by urine leakage when the bladder fails to empty after urinating. Often, people with overflow incontinence wet themselves without feeling the urge to urinate. It typically occurs when urine is blocked from entering the bladder normally. In addition, prostate enlargement, which can close the urethra and muscles interactiveness, can cause overflow incontinence.
The condition is often related to cardiovascular and diabetes diseases. Although it affects everyone, overflow incontinence is a rampant issue for men, mostly because it’s linked to prostate conditions. Besides enlarged prostate, other causes of urine blockage are bladder stones, scar tissue, multiple scrolls, aging, and tumors.
While less common in women, uterus prolapse could cause the urethra to slightly kink (narrow), interfering with the usual urine flow. To put it in perspective, you can think of the urethra as a garden hose. Narrowing in the hose damages the structure, leading to issues like urethral leaking, pain, and urine stream spraying.
4. Functional Incontinence
It’s caused by illnesses other than a misfunctioning urinary tract. In other words, the victim has other conditions that keep them wet often, called functional incontinence. Conditions like mental illness, dementia, or other medications that can render you unaware of the need for a bathroom break could make you continent. Even when the urinary stem functions properly, you find it difficult to get to a washroom to relieve yourself.
Medications like diuretics, used to treat heart failure or high blood pressure, can cause discharges of large amounts of urine, developing functional incontinence. Many people with this condition, therefore, often wet their beds.
5. Reflex Incontinence
Imagine a person who’s wet but can’t tell. Chances are, they’re having reflex incontinence, a condition that causes large amounts of urine leaks without any urge or warning. It primarily follows nerve damage and people with neurological impairments due to spinal cord injury, multiple sclerosis, etc.
6. Mixed Urinary Incontinence
You can suffer from mixed urinary incontinence if ailing from more than one type of incontinence. Most often, a person experiences stress and urge incontinence becoming a more challenging situation. While it’s a dominant issue in women, mixed incontinence can affect men as well, often following surgery, enlarged prostate, or prostate removal.
Causes of Urinary Incontinence
There are several causes of urinary incontinence including:
1. Menopause and Old Age
Menopause and old age are the common cause of urinary incontinence. Various changes occur in the urinary bladder, pelvic floor muscles, sphincters, and ureters as people age and women reach menopause. Often, the changes interfere with the urination tract, leading to incontinence. For example, as men age, the prostate gland usually enlarges, and the vagina prolapses in women, who often present an abnormal descent or obstruction of the urethra.
Another thing is that after menopause, women usually experience decreased estrogen, which can subsequently weaken the sphincters and pelvic floor muscles and, therefore, urine leaks.
2. Heredity
It’s possible to find some members of a family experiencing a form of incontinence, and it’s because this condition is hereditary. So you can expect it in a family with a history of urethra sphincter and weak pelvic floor muscles.
3. Constipation and Chest Infections
Bronchitis, common cold, chronic constipation, and flu are typical chest infections that increase the risks of urinary incontinence. It’s because of the frequent coughing and sneezing that potentially increases abdominal pressure.
4. Obesity
Due to the accumulation of fat, which increases abdominal pressure, the urethra sphincter may lose the ability to keep the urethra closed when a person is lifting weights, walking, or exercising.
5. Smoking and Alcohol
Frequent smokers have a high chance of developing chest infections, coughing, and sneezing. Alcohol users, on the other hand, can experience incontinence following the stimulant effects of these substances to cause inappropriate contractions of bladder muscles.
6. Urinary Tract Infections
One of the leading causes of urinary incontinence is urinary tract infection. The infections usually involve the urinary bladders, urethras, all parts of the urinary tract that includes the pelvic walls. Such an issue if occurs raises sensitivity of your bladders muscles and it contracts abnormally causing incontinence.
Diagnosis of Urinary Incontinence
Urinary incontinence is easily diagnosable, as the primary symptom is an uncontrolled urge to urinate. However, the exact type you are ailing from can often be difficult to recognize, so there is a need for tests and exams.
Some of the ways used in urine incontinence diagnoses are:
- Urinalysis: This involves taking a urine sample to check for abnormalities, traces of blood, and signs of infections.
- Bladder diary: Your physician asks you to monitor your water and beverage intake and the corresponding amount of urine you produce. Also, you’ll record whether you felt the urge or sudden need to urinate to determine the specific incontinence you may be having.
- Postvoid residual measurement: Here, you urinate in a transparent container to see your urine output. Subsequently, your caregiver examines the leftover urine in the bladder using an ultrasound test.
When there is a high amount of urine left in the bladder, there could be a possible obstruction with your bladder muscles or nerves, suggesting what incontinence you have.
When more examination is required, your doctor can recommend aerodynamic and pelvic ultrasound tests, among other more involving tests, most of which involve surgery.
Treatment of Urinary Incontinence
First, urinary incontinence is treatable and manageable, so you shouldn’t worry. Secondly, various treatments depending on the exact incontinence, underlying cause, other medications, and severity. Often, a combination of treatments is used.
The primary treatment methods are lifestyle change, medications, surgery and absorbent pads.
1. Lifestyle Change
Changes to your lifestyle can significantly manage incontinence. The changes can help strengthen the pelvic floor muscles and the urinary tract. Before you can take this treatment, though, seek more guided lifestyle changes from your doctor.
Some of the life changes to help manage incontinence include:
- Avoiding lifting heavy materials
- Maintaining a healthy weight
- Urinating on a planned schedule
- Urinating before physical activities
- Doing kegel exercises often
- Wearing pads and adult pull to avoid leaking urine
2. Medications
Urinary infections can be managed with medications and drugs. The absolute focus of the medications is to prevent leaks and stabilize the bladder muscles to prevent over and under-reactiveness. Others are meant to relax your muscles for optimum bladder emptying.
With the right medication and drugs, your bladder can function as normal as before. Doctors often start with low doses and subsequently increase them when necessary to reduce the risks of side effects and monitor if a typical medication works for you.
The various medications used to treat urinary incontinence include:
- Alpha-blockers
- Mirabegron
- Anticholinergics
- Topical estrogen
- Electrical stimulation
In addition, medical devices like urethral inserts, pessary, and vagina inserts can be used with the medications above.
Other doctors can recommend interventional therapies like bulking materials injections, OnabotulinumtoxinA, Nerve stimulators, etc.
3. Surgery
Surgery is often the last option when all others have failed. Your doctor may recommend a simple or a more complex surgery depending on the procedural option available, symptoms, the type of incontinence, and other medications.
The various surgery procedures available for incontinence include:
- Sling procedures
- Bladder neck suspension
- Artificial urinary sphincter
- Prolapse surgery
4. Absorbent Pads
In case your incontinence issue doesn’t get easier after all the babble options, consider absorbent products like adult pull-on diapers. They help in promoting comfort and convenience when urine leaks. The good thing is that they are simple, comfortable to stay in, and unnoticeable.
A catheter is another typical absorbent tube you may want to use, especially if the incontinence is caused by the bladder not emptying. Ideally, put this tube in the ureter to drain the bladder and repeat the process after a thorough cleaning.
Conclusion
Starting medication is easier when you know what urinary incontinence is, its signs, and the diagnosis procedures. Urinary incontinence shouldn’t be a death sentence or an issue that can limit your involvement in your daily routines. With a clearer picture, you can better manage the condition or care for your loved ones.
Remember, an adult pull-on diaper could be all you need to manage incontinence problems following its absorbency, wetness indicator, comfort, and flexibility.