In this article, we’ll look at a brief summary on spoofing and how to prevent it. If you’ve ever logged into your computer only to discover that your IP address has been spoofing, you must protect yourself. Spoofing attacks can be carried out in many ways, such as Email spoofing, DNS cache poisoning, and even text messages. Here are some tips for protecting yourself. Once you know how to prevent these attacks, you’ll be on your way to protecting your privacy.
What is Spoofing?

Spoofing is an internet fraud technique in which an attacker pretends to be another entity, such as a website or local number, in order to get the victim to click on malicious links or divulge sensitive information. Such frauds may install malware on the victim’s device or spy on their personal data without their knowledge.
Types of Spoofing
1. Internet Protocol (IP) spoofing
Understanding the process of IP spoofing and ways to prevent it is crucial to protecting your network from cybercriminals. It works by analyzing the headers of each packet to identify any suspicious information. By analyzing these headers, hackers can hide their presence and deceive computer systems into believing they are from the other side of the world.
IP spoofing is an attack at the network layer, which is Layer 3 of the Open Systems Interconnection communications model. The attacker sends packets to the target from many different devices. Because these packets can be difficult to trace, blocking the IP spoofing attack is nearly impossible.
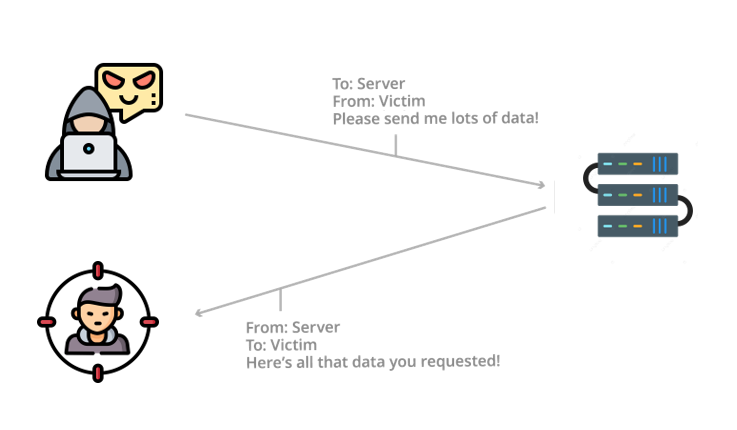
If an IP spoofing attack succeeds, it will take advantage of a trusting relationship between the attacker and the victim. They can even personalize messages, so the recipient thinks they are from a trusted source. This attack is becoming more common as remote workers become increasingly mobile, and even a single device can compromise your network. In addition to the risk of spoofing, knowing how to protect yourself from phishing attacks is essential.
2. DNS cache poisoning
In case you’re wondering how DNS works, a DNS packet consists of three parts: a header, a question section, and an answer section. This packet is generally made up of 512 bytes and consists of three separate parts. The title is always 12 bytes long, but the question and answer sections vary in size. DNS queries and responses are generally carried out over UDP (universal-draft-protocol), which is why the TTL of the packets is 512 bytes. The answer section is usually the most valuable part.
There are several ways to prevent DNS cache poisoning in your computer. You should configure your DNS servers to rely less on relationships with other DNS servers. This makes it harder for cybercriminals to corrupt your target and reduces the likelihood that a website will redirect you to the wrong domain. Here are the main ways to prevent DNS cache poisoning. These tips should be followed to keep your computer secure. The first step is to learn how to identify and prevent DNS cache poisoning.
3. Email spoofing

Email spoofing in computers is a scam in which an attacker can mimic a legitimate company email address, such as a bank. The spoofed email may even have the company logo and persuasive language to convince the recipient to act quickly. Ultimately, it is the recipient’s responsibility to take action and report the scam to the proper authorities. Thankfully, there are ways to prevent email spoofing on computers and protect yourself.
One of the most common ways to spot a spoofing email is to examine the sender’s email. Most legitimate emails will address you directly, and if you are suspicious of an email, check the sender’s website. Moreover, it would help if you looked for unusual sentence structures or poor spelling. If the email sounds urgent, it is spoofing. As such, you should act immediately to protect yourself.
Keeping your software up-to-date is another way to protect yourself. Regular updates include security patches, bug fixes, and new features. Regular updates also minimize the risk of malware infection. You should also avoid visiting websites with poor spelling, unclear grammar, or missing content.
4. Text message spoofing
The most crucial tip when spoofed SMS messages occur is never to click on links that appear in the SMS. For example, if you receive an urgent SMS requesting your personal information, never click on the link. Instead, visit the company’s website directly. And if you receive an SMS asking you to enter your password, do not click on it. Such SMSs are almost always scams.
In addition to following the steps described above, you should also be cautious about sharing your phone number. Only give your phone number to people who need it urgently, and make sure that no one else is spoofing your number. This way, if you get a spoof message from a friend, you can prove it is not them. It is important to remember that spammers can even change the name of the person who sent it.
5. Caller ID spoofing
You may be concerned about Caller ID spoofing in spoofed phone calls for many reasons. For example, a business might copy a number with malicious intentions, such as making unsolicited telemarketing calls. This can damage a business’s reputation, but cybercriminals can also use it to pretend to be an entity they aren’t. Fortunately, there are several ways to detect and prevent this problem.
Another common way to get scammed is by phoning businesses. Many scammers use spoofing to pose as an official organization, such as the IRS, and demand sensitive information such as credit card numbers or bank account information. This type of fraud can lead to identity theft or fraud. It would help if you took precautions by limiting your caller IDs to protect yourself and your business.
6. Website spoofing
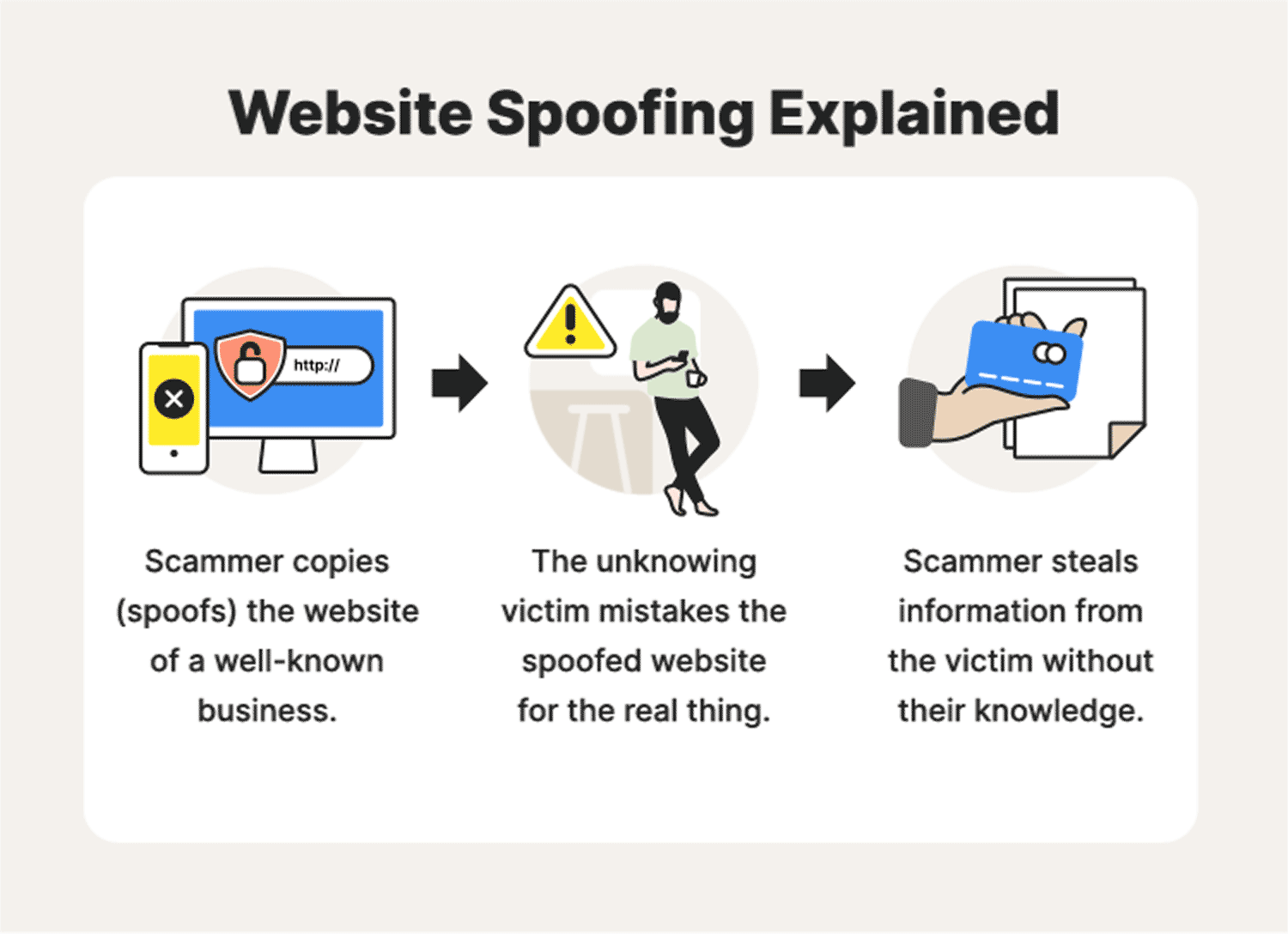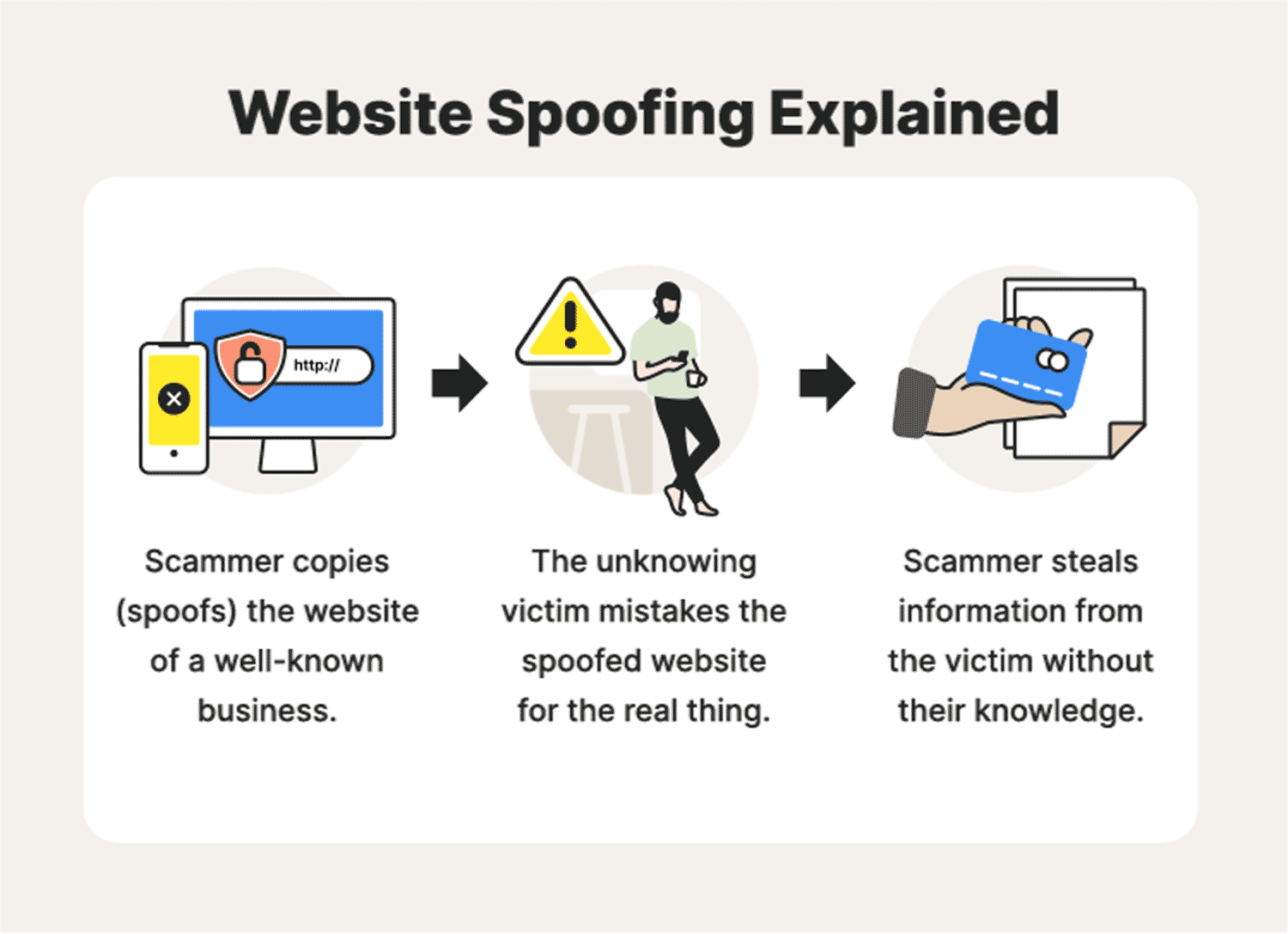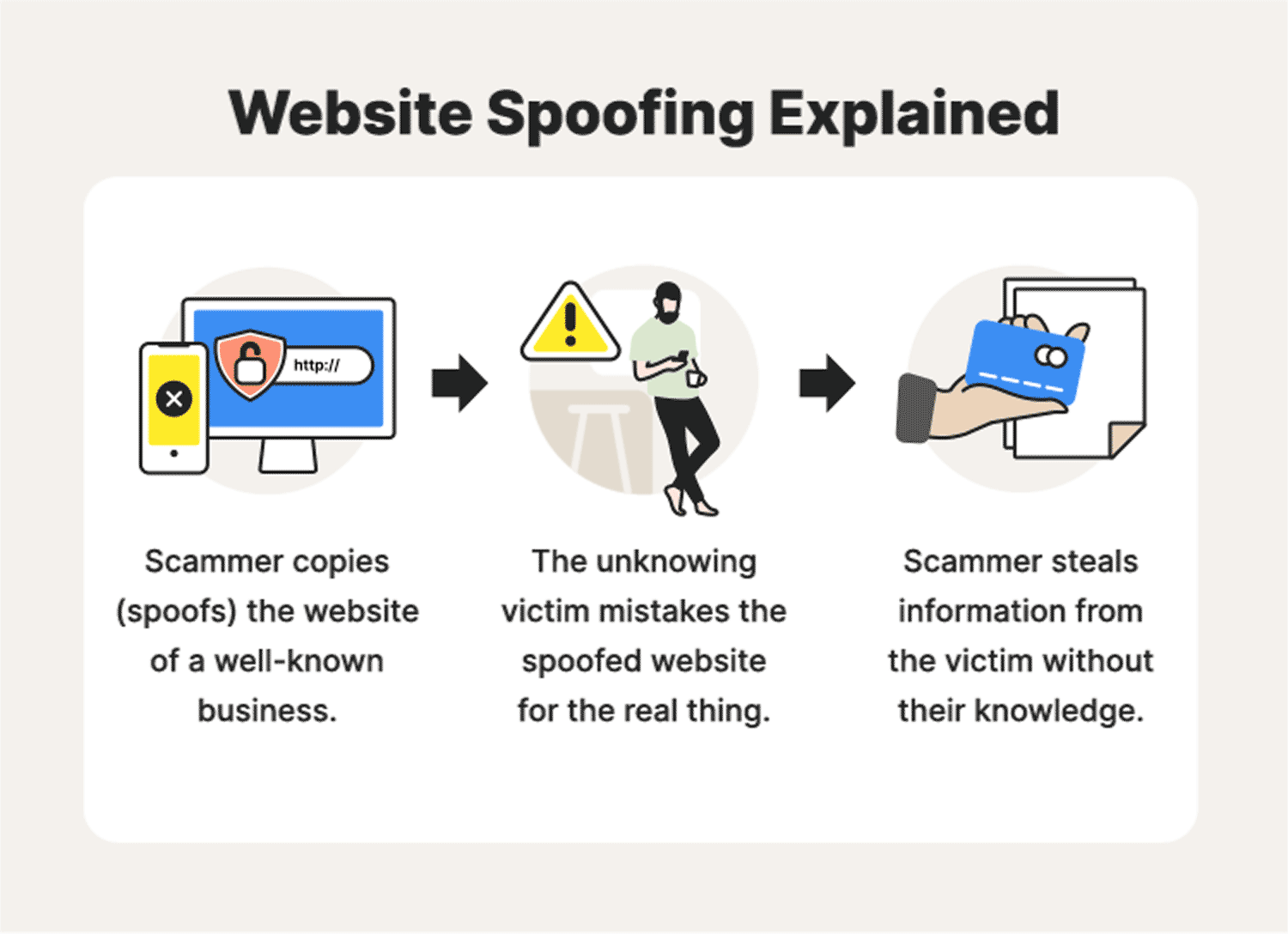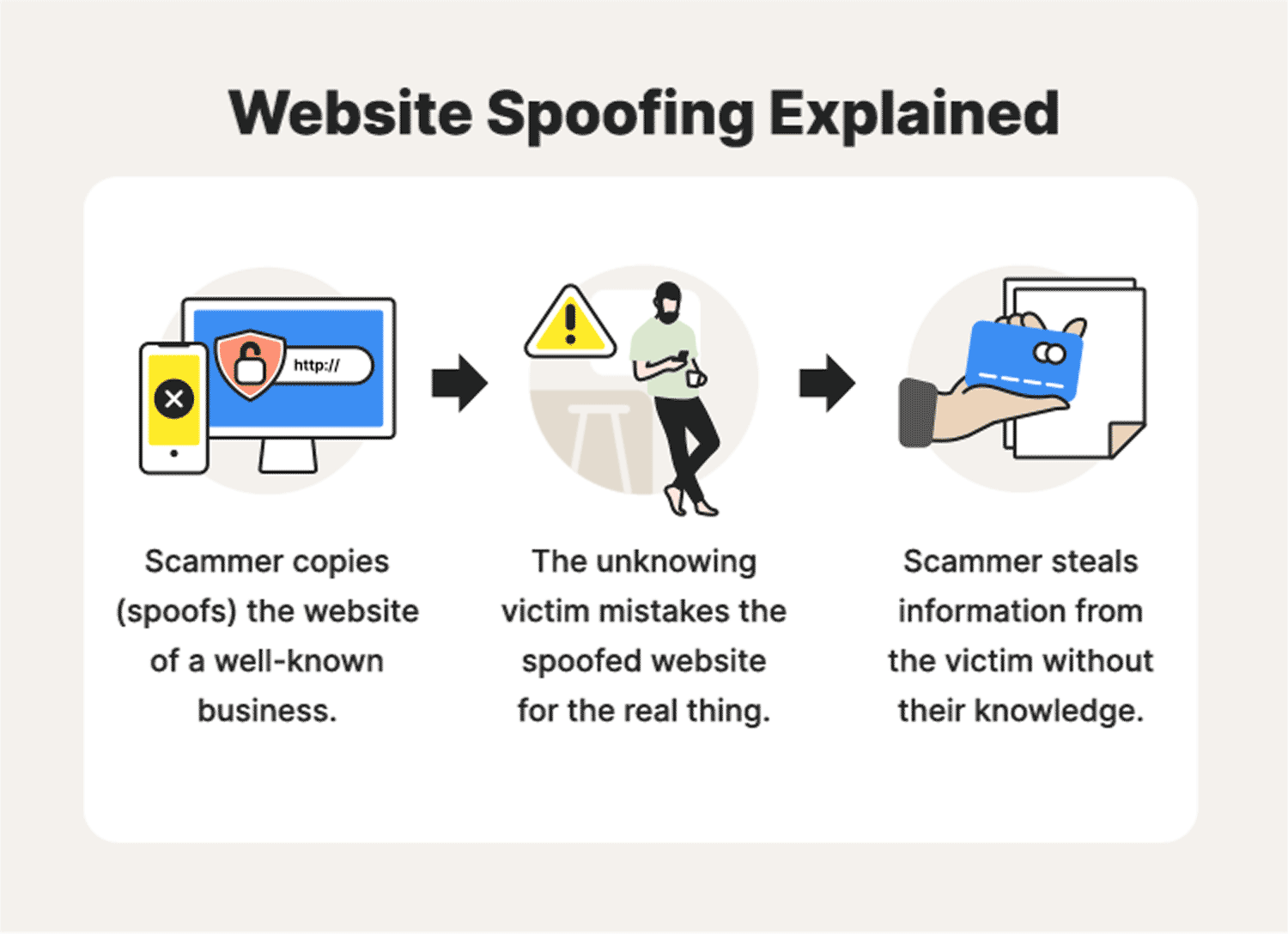
How to detect website spoofing on a computer, how to identify spoofed sites, and how to avoid being scammed by fake websites. To spot a spoof website, look for an HTTP prefix at the beginning of the URL. This means the website is not encrypted, so hackers don’t bother.
The goal of a spoof attack is to steal sensitive information. This information is used to commit fraud and to commit identity theft. The purpose of the spoofing attack is to exploit a user’s fear of an unknown website. By posing as the website of a trusted organization, spoofers can trick the victim into visiting a spoofed version of the website.
Using clever spelling tricks, they can even pass off the fake site as a legitimate website.
7. GPS spoofing
The first step in GPS spoofing is to generate a false signal by modifying the time-stamp of the real one. This is usually accomplished by adding a time-stamp later or earlier than the actual one, keeping the original GPS time-stamp unaltered. Another approach is to add a fixed propagation delay for each satellite, resulting in a spoof GPS signal. This approach is not difficult to carry out, but it is still dangerous.
This technique is illegal unless the device’s owner authorizes it. If you intend to spoof someone else’s location, you are prohibited from doing so. Although this method is illegal, you will not be asked about it when you try it yourself. Spoofing apps, like Pokemon GO, are popular targets, but you may not want to violate the terms of service for these apps. You risk getting your account banned or even banned entirely if you do.
While GPS spoofing has been around for decades, it has only recently become widespread. The military uses encrypted versions of GPS for several purposes, and transportation and logistics use backup systems, such as paper charts. But many commercial applications do not have military-grade encryption. As a result, it is hard to find alternatives to GNSS that are practical for everyday use. The current estimate is that there are already 6 billion GNSS sensors in devices, with an additional 8 billion expected by 2023.
How to prevent Spoofing?
One way to combat IP Spoofing is to use Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) authentication, which uses a private and public key pair to encrypt and decrypt communications. To protect your network from spoofing, you should install network monitoring technologies.
A way to prevent DNS cache poisoning in computers is to make sure that you update your computer’s antivirus software regularly. By doing this, you will not get a security breach but still, have your device protected. This attack is a significant threat to your computer and should be taken seriously. DNS cache poisoning can be an essential source of security risk, and this vulnerability can also lead to privacy violations or even identity theft.
To avoid being a victim of email spoofing:
- Be vigilant and hide your IP address when browsing the internet.
- Do not click on the link or open the attachment if you suspect an email.
- If the email has an unusual file extension, do not open it. You should also ensure that your website has a secure SSL certificate.
An important tip for preventing SMS spoofing is blocking numbers with the same country code. Another thing to do is check the number in your address book. You can even request a PIN from the sender. This is a way to ensure that the person you’re talking to is not sending you spam. Lastly, never click on an embedded link in an SMS. It may be an innocent-looking website, but it’s never safe.
One way to protect yourself from caller ID fraud is to install a security program that detects spoofing calls. This software will automatically identify suspicious calls. By limiting your computer’s caller ID to a few specific numbers, you can tell the difference. You can also set your firewall to block unauthorized caller IDs, and you’ll get a notification when anyone tries to call you.
A way to spot a spoof website is to check for errors. Also, if a website you use has a strange domain name, it is probably a spoof. Usually, you’ll notice that the URL doesn’t have the exact domain name you’ve typed in and doesn’t autofill any of your personal information.


