With so much stuff on the internet, some of it isn’t helpful and can even be harmful. Instances include websites featuring explicit content, engaging in fraudulent activities, or hosting malware that poses a risk to your system.
Many modern web browsers, such as Google Chrome, provide features allowing you to limit access and block undesirable web pages.
To assist you in this, we will explore some methods to block websites on Chrome.

Block Websites on Google Chrome Using an Extension
- Navigate to the website you want to block.
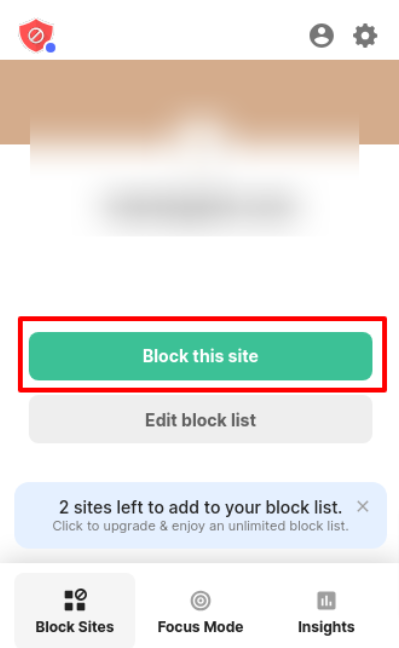
- Select the BlockSite icon located at the upper right corner of your browser.
- Click on the “Block this site” button to restrict access to the website.
- Upon adding the site to your block list, BlockSite will display a notification page, as illustrated below.
We suggest utilizing BlockSite, a highly popular website-blocking extension.
Enter “BlockSite” in the search bar, and select the appropriate result on the right.
Next, click the “Add to Chrome” button located in the upper right corner and patiently wait for the extension to complete its download.
BlockSite will be included in your list of Chrome extensions upon download completion.
You can also include a website URL in your block list by accessing the BlockSite dashboard. Select “More options” on the BlockSite extension and click “Options“. You can block websites within the “Block Sites” tab by entering their URLs in the provided field.

If you want to restrict access to the websites on your block list even in Chrome’s incognito mode, click the gear icon for the extension Settings, then select the “Enable in Incognito Mode” option.
Moreover, BlockSite offers the following functionalities for Google Chrome:
- Focus mode – temporarily block sites by setting a timer. You can establish intervals between focus modes to browse without restrictions during breaks.
- Block by words – prevent access to a website with a domain name or URL containing specific words or phrases.
- Categories – block numerous sites of the same category, such as adult, social, news, sports, and gambling.
- Redirect – reroute access from blocked websites to a different address based on your configuration.
- Scheduling – restrict access to websites only within a specific schedule of your choosing.
Block Sites on Chrome for iPhone and Android
BlockSite is also accessible as a mobile app, allowing you to block websites or apps on your mobile devices. This can be convenient as the interface is familiar, especially if you’ve used the Chrome extension. To block websites on your Android device, follow the below steps:
- Go to the Google Play Store on your mobile device and locate the BlockSite app. Click on “Install“.
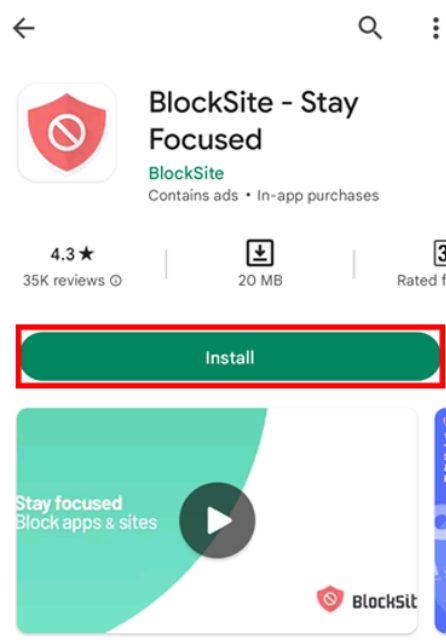
- In your device settings, permit the installation of the BlockSite app and then open it.
- Identify the green plus icon within the app to block websites or apps.
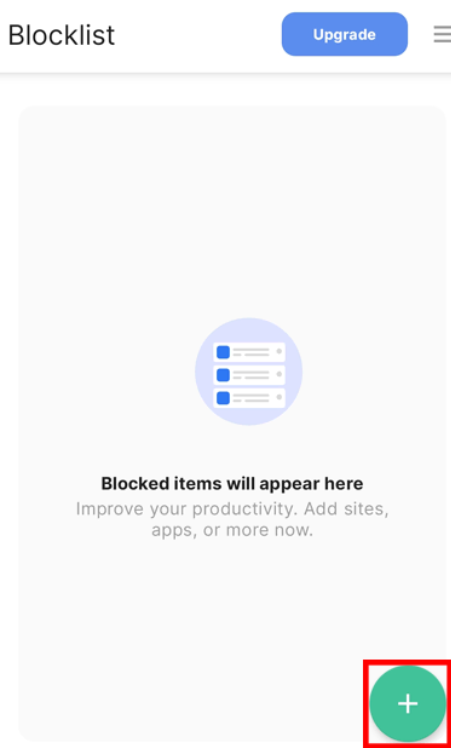
- Enter the desired keyword or domain name for blocking. You can also block specific applications by selecting icons under the “App Suggestions” section.
- Tap “Done” once you have completed the blocking process.
- Check the results by attempting to access the website or application through your browser or app. BlockSite should display a block page.
For iOS users, follow the steps mentioned above, but visit the Apple App Store to find and install the BlockSite app for iOS.
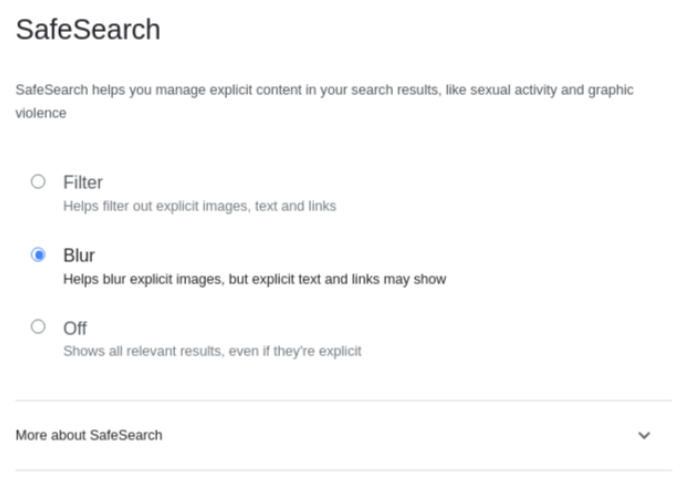
Block Websites on Chrome using the SafeSearch feature
Using the SafeSearch feature, you can easily restrict access to specific websites on your Chrome browser. Go to your computer’s Google account preferences and check the terms Filter, Blur, and Off.
Block a Site by Editing the Host File
An alternative method for blocking a website on your device is by modifying the host’s file. This local text file within the operating system holds domain names and their corresponding IP addresses.
Before making edits to the host’s Windows file, ensure you use an administrator account. The procedure is simple, involving the addition of the specific website URLs directly into the file.
On Windows,
- Go to the File Manager and access C:\Windows\System32\drivers\etc. Open it with the text editor.
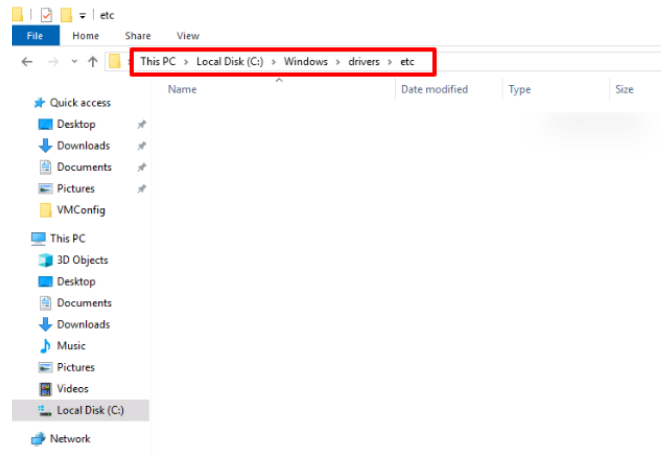
- At the end of the file, below the last #, insert new lines and enter your localhost IP address (127.0.0.1) along with the website domain you want to block.
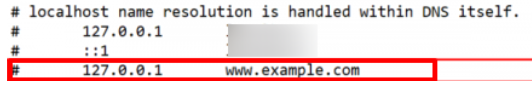
- Save the File. Save the file without using the .txt extension, as it won’t be effective with that format.
- open Chrome and enter the blocked domain to check if the block is effective.
- If you wish to block additional websites, simply repeat the process by adding new lines.
On MacOS,
For macOS users, blocking websites on Google Chrome through the host file follows a similar procedure.
- Open Utilities > Terminal.
- In the Terminal command, input sudo nano/etc/hosts. This action opens your host’s file in a nano box.
- Provide the administrator password to access your host’s file, which should contain several lines resembling the format used in Windows.
- At the end of the last line, enter the localhost IP address 127.0.0.1. After pressing Tab for space, type the site’s domain name you want to block.
- Repeat the process if you want to add more sites.
- To save, press CTRL + O.
- Exit the host’s file by pressing CTRL + X.
- To avoid conflicts, clear your cache by entering sudo dscacheutil -flushcache and pressing Enter after completing the steps.
- Open a browser to test the results.
Blocking Websites on Chrome with the BlockList URL Feature
As an administrator who manages Google Accounts for your organization, you can use Chrome’s BlockList URL feature through your Google Admin Account to restrict access to specific websites.
This approach proves highly efficient when dealing with numerous devices, eliminating the need to block websites on each individually. To use the BlockList URL feature, proceed with the following steps:
- Access your Google Admin Console by visiting admin.google.com using your web browser.
- On the Home page, go to Devices > Chrome > Settings > Users & Browsers.
- Choose the primary organizational unit to block website access for all Chrome users using the organization’s Google service.
- Select a child organizational unit if you aim to block websites for specific individual users.
- After choosing the appropriate organizational unit, scroll down to locate the URL Blocking section.
- Under the URL blacklist, input the URLs to initiate the blocking of websites on Chrome browsers across your organization. As demonstrated in the example below, you can also block URLs for specific services, such as browser settings.
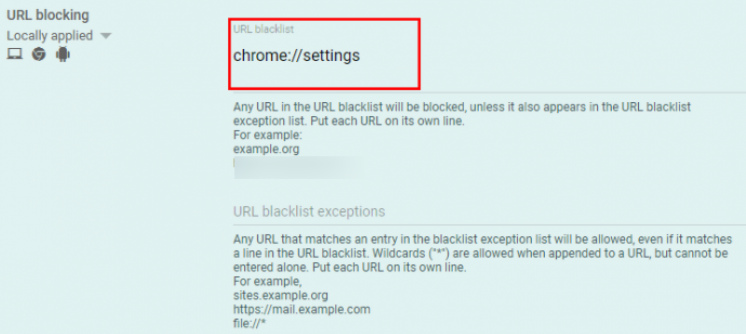
- Verify on one device to confirm the successful implementation of website blocking using this approach.
Block Websites on Chrome With the Built-in Parental Controls
Parental Control is a notable feature in various modern devices and software. It is an excellent tool for restricting children’s device usage time and overseeing the content they can access.
This guide will walk you through setting up parental controls on Windows 11 and Google Chrome. Notably, macOS comes with its built-in parental control feature known as Screen Time; however, it does not extend to blocking sites on Chrome.
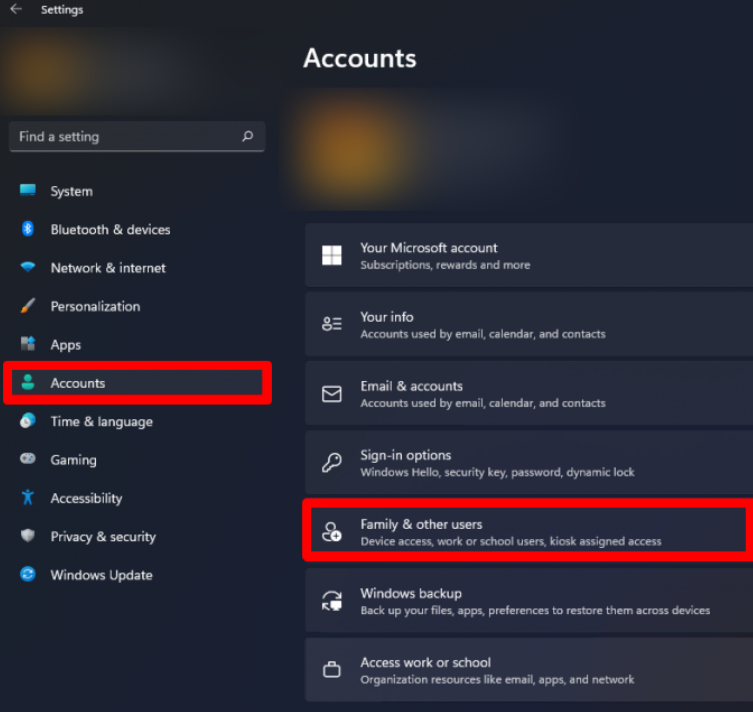
- Navigate to Settings in the Windows menu, then go to Accounts to establish a child account.
- Click on Family & Other Users, Add a family member, and select Add Account.
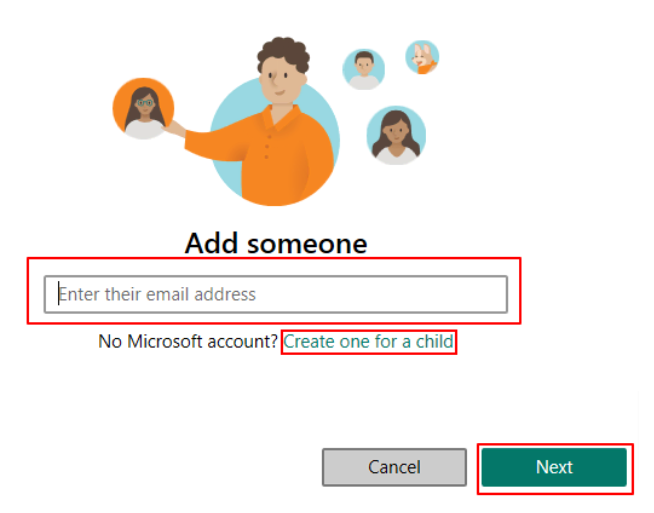
- In the new window, enter your email and select the Create one for a child option.
- Access the newly created child account through your Microsoft account page.
- Proceed to Content filters > Blocked Sites, input the URL or domain name of the site you want to block.
- Click the plus icon to add it to your block list. Repeat this process for additional sites.
- Verify the results by switching to your child’s account and confirming whether the designated site is successfully blocked.
To restrict a website using Google Family Link, follow the below steps:
- Download the app from the Google Play Store and establish a family account.
- Access your child’s account.
- Navigate to Manage Settings > Filters on Google Chrome > Manage sites > Blocked.
- Tap the Add an Exception icon.
- Enter the website or domain you intend to block.
- Save the changes and verify whether the site is successfully blocked.
What Could Be the Reasons for Blocking Websites?
- Content Restriction: Limiting access to certain websites can be essential to protect users from specific web content. For example, parents may restrict access to adult websites on family devices.
- Malicious Sites: Computer viruses harm your device and can sometimes slip by antivirus programs. If you identify particular websites that could contain malware, it’s crucial to block them promptly.
- Work Mode: Enabling website blocking can enhance productivity by minimizing distractions. Individuals can concentrate better on tasks with fewer distractions on their phones or desktop computers.
Conclusion
In conclusion, blocking a website on Google Chrome offers various methods to suit different preferences and needs. Whether you opt for manual edits in the host file or leverage the BlockList URL feature through the Google Admin Console, each approach provides a tailored solution. By incorporating these techniques, users can enhance security, control content access, and foster a more focused and productive online environment. The flexibility of these methods ensures that individuals and administrators can find an effective way to manage website access on the Chrome browser.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What are the best website blockers?
The best website blockers are SiteBlock, Serene, Freedom, and Y-Productive. These blockers are accessible as applications for installation on your device, and some are compatible with different OS (operating systems), such as Windows or Mac.
2. Are there any limitations to block websites on Google Chrome?
While blocking websites is effective, it’s crucial to acknowledge that resourceful users may discover workarounds. The effectiveness of website blocking can be improved by employing various methods or utilizing third-party applications.
3. Is it possible to use Chrome to protect against malware and inappropriate content?
Yes, blocking particular websites can act as a preventative measure against malware, shielding users, particularly underage individuals, from accessing inappropriate content.